Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Sulfur tetrafluoride
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Sulfur tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas upon exposure to water or moisture. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds,[3] some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.
Remove ads
Structure
Sulfur in SF4 is in the +4 oxidation state, with one lone pair of electrons. The atoms in SF4 are arranged in a see-saw shape, with the sulfur atom at the center. One of the three equatorial positions is occupied by a nonbonding lone pair of electrons. Consequently, the molecule has two distinct types of F ligands, two axial and two equatorial. The relevant bond distances are S–Fax = 164.3 pm and S–Feq = 154.2 pm. It is typical for the axial ligands in hypervalent molecules to be bonded less strongly.
The 19F NMR spectrum of SF4 reveals only one signal, which indicates that the axial and equatorial F atom positions rapidly interconvert via pseudorotation.[4]

Remove ads
Synthesis and manufacture
At the laboratory scale, sulfur tetrafluoride is prepared from elemental sulfur and cobaltic fluoride[5]
- S + 4CoF3 → SF4 + 4CoF2
SF4 is industrially produced by the reaction of SCl2 and NaF with acetonitrile as a catalyst[6]
- 3 SCl2 + 4 NaF → SF4 + S2Cl2 + 4 NaCl
At higher temperatures (e.g. 225–450 °C), the solvent is superfluous. Moreover, sulfur dichloride may be replaced by elemental sulfur (S) and chlorine (Cl2).[7][8]
A low-temperature (e.g. 20–86 °C) alternative to the chlorinative process above uses liquid bromine (Br2) as oxidant and solvent:[9]
- S(s) + 2 Br2(l; excess) + 4KF(s) → SF4↑ + 4 KBr(brom)
Remove ads
Use in synthesis of organofluorine compounds
In organic synthesis, SF4 is used to convert COH and C=O groups into CF and CF2 groups, respectively.[10] The efficiency of these conversions are highly variable.
In the laboratory, the use of SF4 has been superseded by the safer and more easily handled diethylaminosulfur trifluoride, (C2H5)2NSF3, "DAST":[11] This reagent is prepared from SF4:[12]
- SF4 + (CH3)3SiN(C2H5)2 → (C2H5)2NSF3 + (CH3)3SiF
Other reactions
Sulfur chloride pentafluoride (SF
5Cl), a useful source of the SF5 group, is prepared from SF4.[13]
- SF4 + Cl2 + CsF → SF5Cl + CsCl
Hydrolysis of SF4 gives sulfur dioxide:[14]
- SF4 + 2 H2O → SO2 + 4 HF
This reaction proceeds via the intermediacy of thionyl fluoride, which usually does not interfere with the use of SF4 as a reagent.[6]
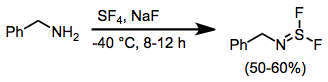
When amines are treated with SF4 and a base, aminosulfur difluorides result.[15]
Remove ads
Toxicity
SF
4 reacts inside the lungs with moisture, forming sulfur dioxide and hydrogen fluoride which forms highly toxic and corrosive hydrofluoric acid [16]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads




